| |
Issues
in loudspeaker design -
7
| Page 1 | Page 2
|
Page 3 | Page 4 | Page
5 | Page 6 | Page 7 |
A2 - High-frequency down-shelving for
ORION-3
B2 - What is the optimum polar response
for a loudspeaker?
C2 - L-07 Dipole loudspeaker
D2 - Phase shift due to dipole D and its
effect upon crossovers
E2 - Sound
field control
F Woofer
equalization in LXmini
G2 - Power amplifier distortion at 1 W
& 100 mW output
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A2 - High-frequency
down-shelving for ORION-3
After having spent many hours of critical listening in the
last two weeks, exchanging observations with Don Barringer, fine tuning the
frequency response and finally launching ORION-3 I
have accumulated many observations and thoughts that I want to convey before
they are forgotten. With ORION-3 I have corrected deviations from flat frequency
response in the two octaves from 500 Hz to 2 kHz. I confirmed that an overall
flat on-axis frequency response is not optimum in a reverberant room and that
there has to be some kind of response shaping for frequencies above 1 kHz. We
found that a small amount of high frequency roll-off was necessary and that
particularly the center frequency of the shelving filter was extremely critical.
Moving the center from 5.4 kHz to 4.4 kHz, a -1.78 dB or 1/3rd octave shift of
the roll-off contour along the frequency axis, changed the perception from
neutral and non-engaging to still neutral, but alive. What is going on? Clearly
the on-axis frequency response is the dominant parameter for a loudspeaker, and
what about the off-axis or power response?
For these listening tests the loudspeakers and listener
formed an equilateral triangle, but not exclusively. Don and I are located
across the country from each other. My room is larger and more live than his.
Don as a former musician and later a recording engineer listens acutely for the
believability of instrument sounds and their spatial context, having the benefit
of years of exposure to acoustic instruments and performers. I am basically a
listener in the audience and predominantly to classical music. I am very
familiar with the sound of instruments in a concert hall and from a distance and
listen globally. After the ORION was equalized to flat I listened to it in my
room and for a while became totally intoxicated by the rush of high frequency
energy. Don pulled me down, rightfully so, because what I heard was not real and
I had known from before that flat is too much. So we turned down the tweeter
level but could not find the right level. There remained an unpleasant
shrillness and the speaker became either dull or had too much sibilance.
I realized that the mid to high frequency transition
changed too abruptly with tweeter level change. We set the tweeter for a flat
response and then added a down shelving filter, which gives a much more gradual
transition that can be easily adjusted for its center frequency and amount of
change. As a starting point for trying different amounts of shelving I decided
that each filter could only be 0.5 dB down at 2 kHz. We immediately heard an
improvement over the tweeter level adjustment results. But then it took many
hours of listening, many phone conversations to arrive at a contour that we both
felt happy with. I went out for dinner to celebrate (my wife was in Europe and I
had gotten really tired of preparing my own vegetarian dinners, which tasted
mostly like rabbit food).
Next day we listened again and there was still some
shrillness, shouting and shrieking, a steely-ness when playing at realistic
volume levels, though much less so than when we started with the equalization. A
female voice in particular is capable of producing some very aggravating high
pitched sounds at high volume levels in real life that I do not like to hear,
but a trained soprano is also capable of a very pleasing high volume voice,
short of piercing. So we continued with our equalization experiments. I focused
very much on female voice, single and in groups, male and female choirs, using
recordings done with sphere microphones and other essentially 2-microphone
recordings that we were familiar with or knew their origin and lack of
post-processing. We focused on strings, harp, brass. In the end I knew we
had come up with something that worked exceedingly well for me and also for Don
and it was "time again to shoot the designer" as we used to call it at
HP. It was time to launch ORION-3 so that others could hear - or not hear - what
we had arrived at. Time for a public beta-test to see if our highly critical
shelving filter travels well and can duplicate our auditory experiences. Let's
call this filter DSS (yes, it also de-esses), short for "Don &
Siegfried's Shelf" because it may be unique to the ORION and /or to the two
of us. The DSS works for us, but it also carries universal aspects. I suspect
that the "BBC Dip" is related, because of its ability to control poor
recordings. I have used a 2760NF for the dip in the PHOENIX
loudspeaker response, but was never as certain about leaving it in the circuit
permanently as I am about the DSS. From what I have heard so far the DSS does
absolutely no harm to excellent recordings. It is necessary.
B2 - What is the optimum
polar response for a loudspeaker?
With the modified ORION I was able to play music at at
volume levels that I had never tolerated before because they made me feel
uneasy, gritting my teeth. This time I was completely at ease, though the volume
must have been near the breaking point for the tweeters. I had myself an
experience, rocked with the music, was completely inundated by it. It was fast
and immediate. It occurred to me later that the speakers did not shout and
shriek at me as speakers tend to do at very high volume level. The room was completely
awash with sound, the room was not even there. The various phantom sources sat
there, solidly defined in space. I could get drunk on this. Why were they not
yelling?
It came to me on the way to the airport, sitting in
traffic: Every sound source has a Gestalt. A violin, piano, human voice etc.,
they all have a Gestalt and we recognize the nature of the source by its
Gestalt. The Gestalt of the human voice is made up of
many elements, like pitch, articulation, directionality. It can be loud, soft,
hard, shrill, soothing and infinitely expressive of emotions. You can take away
almost all elements and still recognize a familiar voice over a very poor
telephone connection. The Gestalt has unique and generic aspects to it, which
make, for example, a Stradivarius much more unique than the violin that my
granddaughter practices on. Loudspeakers have a Gestalt and that is a problem.
The loudspeaker should reproduce the Gestalt of any source and not add its own
to it. How could that be possible?
Almost all sources that we are familiar with, which means
sources that we have a memory of, are directional although to varying degree.
That is merely a function of their physical size no longer being small compared
to the wavelength of sound being radiated or from using cavities to concentrate
the sound into a beam. It is the directionality of a source, its polar response
that determines how the environment, the room talks back by reflecting the
output from the source. Directionality determines how the room is illuminated
with sound in various directions and therefore how a particular person or friend
sounds in my living room. My room has a Gestalt. The room detracts very little from the Gestalt of his
voice and I am not aware of the room because I am familiar with the room's
Gestalt. We familiarize ourselves very quickly and subconsciously with the
Gestalt of a new space upon entering it. It is a survival mechanism.
When I
hear my visitor from behind the closed bathroom door the Gestalt of the sound that I
hear coming from him has changed, but I can tell whether he is still in the
living room or has stepped outside to the patio while I was away. In other words
I now hear him and the environment he is in. In the living room, my auditory
horizon, my attention had focused on the visitor, ignoring the familiar room.
From inside the bathroom my horizon encompassed the bathroom sounds and the
sounds transmitted into it through the closed door. The visitor's Gestalt had
merged with the Gestalt of his environment. No longer could I tune out the
effect from the cause. When listening to a recording I am always presented with
a cause and an effect, the musical instruments and the response of the
environment they were in. That is what I expect to hear in as much realism as
possible. That is what I have learned from listening to live sources.
Loudspeakers have a Gestalt due to their frequency
response, radiation pattern, distortion, re-radiation, hidden resonances,
diffraction, etc. We do not want to hear their Gestalt, particularly when they
are to create phantom sources as in 2-channel reproduction. Phantom sources,
which are a construct of the mind, are fragile because they have to be
constructed from the cues that left and right loudspeakers provide. Cues that
must match with learned and memorized patterns or must be believable. The
radiation pattern is how the loudspeaker illuminates the room and thereby
imparts this aspect of its Gestalt to the listener. Furthermore this aspect gets
intertwined with the Gestalt of the phantom source, the human voice that hovers
between the loudspeakers and we hear both together, seemingly inseparable. But
they can be separated, if the loudspeaker has a non-intrusive Gestalt. The
radiation pattern must be such that room reflections and energy radiated into
the room do not upset the spectral cues that left and right loudspeakers
transmit to the ear and brain directly. Ideally, reflections should have the
same spectral content as the direct sound, they should be delayed to avoid
fusing with the direct sound and very importantly the power response of the
loudspeaker should be flat. For the loudspeaker designer this means that
the source should be acoustically small, be omnidirectional, dipole or cardioid.
With the Gestalt of the loudspeaker removed from the room reflections the
phantom source becomes defined by the direct sound only. The room itself moves
beyond the perceptual horizon.
Omnidirectional is the mother of all loudspeakers. An omni
can instantly illuminate the room with sound of all frequencies, like an
explosion. It has the ideal spatial impulse response. It generates a fast
response from the room. The dipole is a close second. The cardioid does not see
half of the room and is not a contender for speed. It's Gestalt is too strong.
In practice, the omni cannot dissipate instantly the airborne energy behind the
cone and the structure borne energy in the cabinet, thus smearing the impulse.
The dipole does not have this energy dissipation issue. All vibration energy is
used to radiate sound to front and back. Illumination of narrow regions to the
sides of the room occurs via reflections, thus slightly delaying the total
build-up of sound in the room. In practice a dipole is the fastest of the three
radiator types that have a constant power response.
If a loudspeaker is directional it should not change its
directionality with frequency. The big remaining question is, how much can it
deviate from that and not cause problems in a reverberant environment. I know
that the polar response of the ORION above 800 Hz is only dipole like in that it
has nulls at about 90 degrees off-axis. It has maximum horizontal dispersion
around 2 kHz and then narrows with increasing frequency. When I played ORION-3
at exceedingly high volume levels it did not shout at me. Certainly our work on
the overall frequency response had paid off. I have also associated
"shouting and shrillness" with beaming as in horn loudspeakers and
many box loudspeakers. I know from my own design experience that it was always
beneficial for sonic smoothness to maintain wide dispersion as frequency goes
up. This is consistent with the requirement for constant spectral content of
reflections and constant power response. I am also impressed with how relatively
insensitive PLUTO-2.1 is to placement near room boundaries. It is a fairly
decent omni source because it is acoustically small up to around 4 kHz and
effectively dissipates mechanical and air vibration energy internally. ORION-3 is remarkable to me because of the large amount
of high frequency energy that it can put into the room and thereby not change
its Gestalt. Phantom sources thus approach the high frequency output of real
sources and appear real.
This says to me
that increasing directivity and rolling off the 4p-power response
with increasing frequency is
not the direction to go when optimizing loudspeakers for home applications.
In this context it is educational to revisit the
theoretical 4p-power
response of a dipole as a function of piston diameter and driver spacing when
two drivers are used, which again emphasizes the need for acoustically small
sources to control directivity.
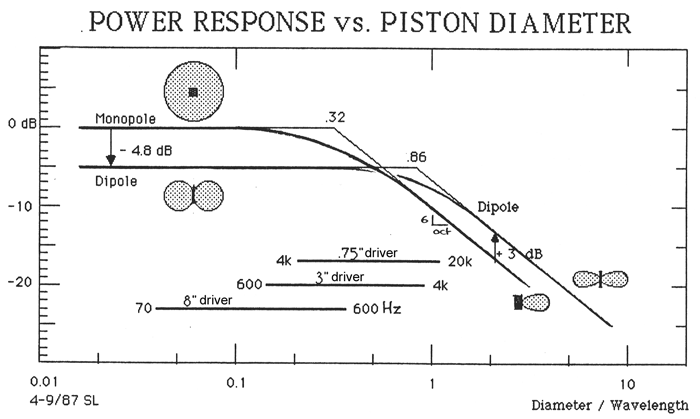
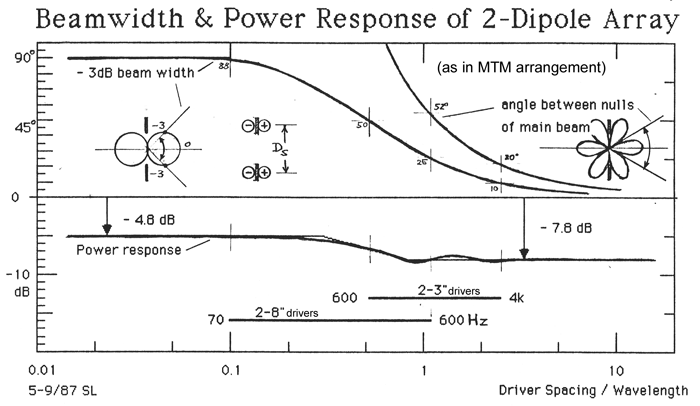
C2 -
L-07 Dipole loudspeaker
In the context of A2 and B2 above, one of my early dipole
loudspeaker designs is of interest. I suspected then that the 4p-power response of the loudspeaker was
problematic, because it defines the interaction with the room. The power
response had to be better controlled, to make it flat and more smoothly behaved
than was typical for loudspeakers of that era. In addition a dipole would reduce
the total reverberant power in the room. Acoustic measurements, though, were
exceedingly tedious with the equipment at hand, therefore the estimates in the
graphs.

The L-07 loudspeakers used front and back 3/4 inch
tweeters, two 3 inch upper mid drivers, two 8 inch lower mid drivers.
The single center woofer had two 12 inch drivers in a sealed enclosure,
tightly placed into a shelf with heavy books stacked on top of it.
Crossover frequencies were at 70 Hz, 600 Hz and 4 kHz. Crossovers and EQ
used TL072 opamp circuits in this 4-way active loudspeaker system. |
 |
.
There was no printed circuit board for the crossover and equalization
circuitry. All the components were assembled on a prototype board front and back with interconnections at
convenient points.
For acoustic measurements I used my shaped-burst generator as source. The
peak amplitude of the received burst was measured in dB SPL with a
threshold detector. The big
knob with the uniform dB-scale was turned until the red LED next to
it just lit up. The data resolution was about 0.5 dB. The burst
frequency could be incremented in 20% steps.
The measured dB value was then plotted on a piece
of graph paper. It took a while to gather all the points for a
measurement from 20 Hz to 20 kHz and to pencil in the resulting curve.
The burst generator method gave better frequency
and spatial resolution than the analyzer we used in the years before.
That one had a pink noise source (a microwave point-contact diode) and a
bank of 24 two-pole third-octave filters with 24 flashlight bulbs as rms
detectors. Their faint glow was adjusted with a dB calibrated gain
control to a reference illumination. The dial reading for each bulb was
then plotted. Russ Riley had designed and hand-wired this tool. It gave
us very useful acoustic measurement capability unlike SPL meters with
their bouncing needle, linear average, display readings.
. |
.

. |
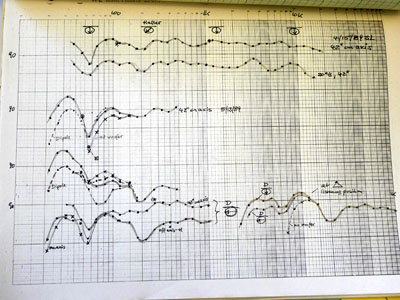 |
 |
Acoustic measurements were tedious and time consuming. I
gladly switched over to the MLSSA Acoustical Measurement System in 1991, though
at a price of $2995 plus $1500 for a PC it was a major outlay for my hobby and
difficult to justify. Only recently and after it was capable of the measurements
that I needed, did I convert to ARTA.
After the L-07 project I adopted Brian Elliott's H-frame
woofers and he adopted a dipole platform for the frequency range above. I did
not use a rear tweeter again until ORION+. Note the narrow upper-mid and tweeter
baffle.
A paper was presented
at the 1987 AES Convention in New York with the title "A Loudspeaker Design
for Reduced Reverberant Sound Power Output". I could not attend and John
Vanderkooy delivered it for me. I talked about the L-07 during an AES Section meeting in 1989.
Subject related presentations were given by Brian Elliott and Floyd Toole.
My designs have progressed since the L-07 and now with ORION-3 I have come to a loudspeaker system that can
play an ever greater variety of program material at exciting loudness levels in
a normal living room.
D2 - Phase shift due to
dipole D and its effect upon crossovers
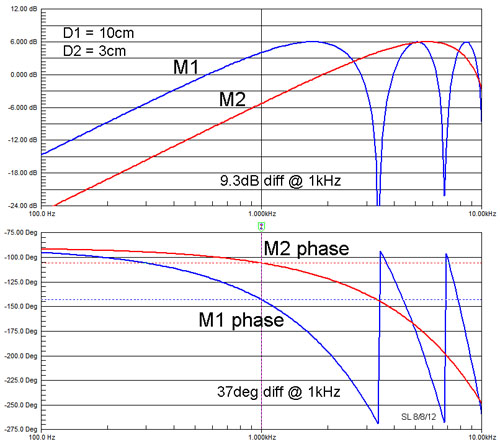
|
Two dipoles M1 and M2
of equal source strength, but different effective distance D between
front and rear sources, exhibit a phase shift relative to each other,
which increases with frequency. This phase shift affects the summation
of low-passed and high-passed dipole outputs.
Here is the example of two ideal dipoles with D1 =
10 cm and D2 = 3 cm to be crossed over at 1 kHz with a first order
Butterworth filter. Only on-axis frequency response curves are shown. We
amplify M2 by 9.3 dB since the higher frequency dipole M2 has less
output at 1 kHz than M1.
|
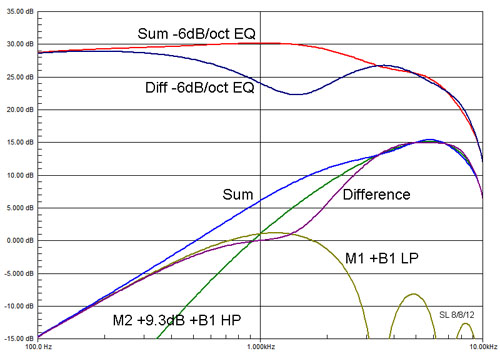 |
The B1 filtered outputs
of the two dipoles have now identical amplitude at 1 kHz. Due to the
additional 370 phase shift their summed output increases by
5.1 dB and not by 3 dB. The output decreases by 1 dB with reversed
polarity of one of the dipoles instead of increasing by 3 dB.
Equalization of the combined outputs at a constant
6 dB/oct rate will not yield a flat response and additional non-minimum
phase equalization is required. Using an offset between M1 and M2 may
cause baffle edge diffraction issues with the adjacent dipole.
Realizable dipoles have additional phase shifts
due to driver responses that affect the crossover behavior on-axis and
off-axis. |
Note: In my original posting I had an error because I only
considered the phase shift of the dipole rear radiation. The resulting analysis
explained well my measured frequency response data for an experimental dipole.
So I felt pretty sure. But if I had also included the phase shifts due to the
bandpass response of my non-ideal drivers, then I might have seen the error. It
was <john k...> on the diyAudio forum, who questioned my explanations, which
helped me to get this right. The above graphs should eliminate any confusion
that was caused.
E2 - Sound field control (here)
F2 - Woofer equalization
in LXmini
 |
The LXmini
evolved from Pluto and provided me with
an opportunity to revisit the woofer equalization using the PEQ functions
available in a miniDSP unit.
Below I explain my design decisions using a CircuitMaker electrical model
(file) of the L16RN-SL driver
in an enclosure.
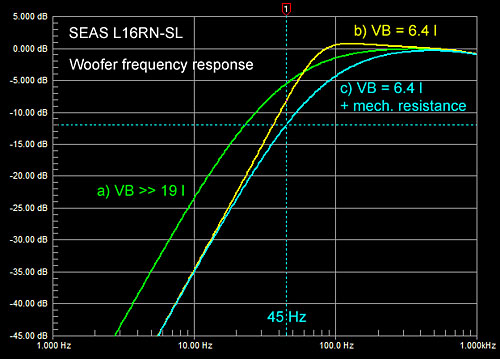
In a very large and sealed enclosure (a) the driver
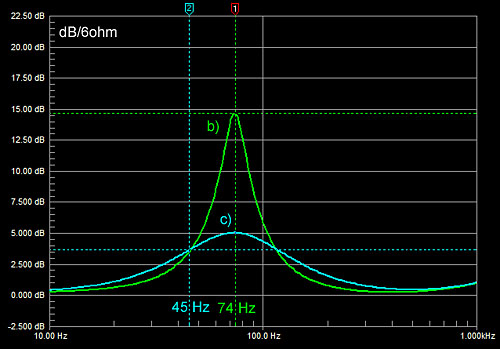
rolls off at 12 dB/oct rate and is about 6 dB down at 45 Hz. When placed
in the 6.4 liter pipe it is about 8 dB down. I am aiming for a 45 Hz, -3
dB corner frequency and equalization becomes necessary to obtain that. |
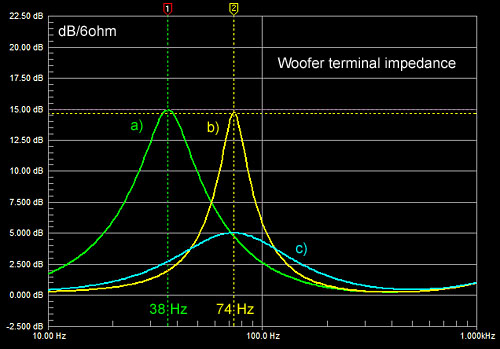 |
In a very large enclosure
(a) the mechanical resonance occurs at 38 Hz, but in the small volume of
the pipe the resonance is pushed up to 74 Hz due to the stiffness of the
enclosed air.
The pipe must be stuffed with acoustic absorbent
material in order to attenuate and suppress standing wave resonances,
which occur at odd multiples of about 110 Hz. The amount of stuffing
affects the woofer's mechanical resonance frequency, first lowering it and
then with more material increasing the frequency. The stuffing also
changes the woofer's frequency response and terminal impedance (c). |
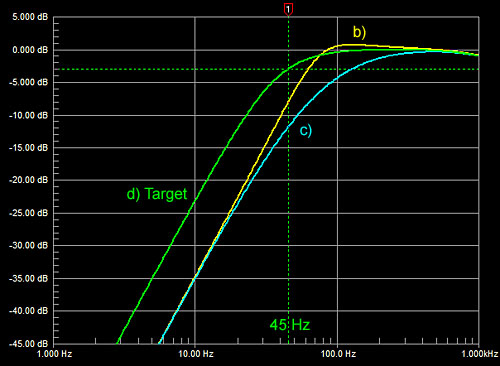 |
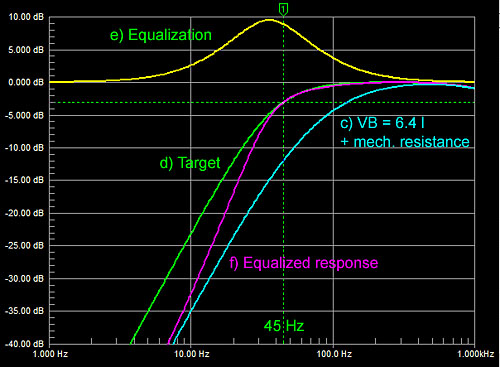
If my target response (d)
is a 2nd order Butterworth highpass filter, then I must add 12 dB of gain
at 20 Hz to (c), 9 dB at 45 Hz, and 4 dB at 100 Hz.
Woofer cone excursion increases as (1/f)2
or at 12 dB/oct rate with decreasing frequency for constant SPL. A
constant drive signal applied to the (d) equalized woofer will thus
require (100/45)2 x 0.7 = 3.5 times the excursion at
45 Hz as it does at 100 Hz and 5.5 times at 20 Hz and below. |
 |
Large excursions below
the driver's mechanical resonance at 74 Hz are especially problematic
because the driver operates in the compliance controlled region, which is
prone to significantly higher distortion than in the mass controlled
region above resonance. It is thus desirable to reduce cone excursions
below resonance.
Around resonance the driver's motion is controlled
by viscous damping or mechanical resistance as in (c). Here is where I was
hoping that increased stuffing might help, though I do not know the
mechanical properties of the material and whether it behaves as viscous or
frictional and whether it has an effect at large excursions. |
 |
Based on the above
considerations I chose to forego the usual "Linkwitz Transform"
biquad and to simply use a bandpass equalization (e). The resulting woofer
response (f) rolls off faster below 45 Hz than the target (d). It starts
at nearly 18 dB/oct rate and gradually returns to 12 dB/oct. I have gained
about a 5 dB (1.8 x) reduction in displacement at 20 Hz and thus very
similar excursion as at 45 Hz for a constant amplitude input signal.
This form of eq also puts less demand on the gain
structure of a DSP unit than the biquad eq.
The faster roll-off below 45 Hz goes with an
increase in group delay and longer ringing in the time domain.
I am pleased with the overall result and perceive it
as an improvement over Pluto in terms of graceful handling of large
signals. But I have not performed comparative measurements between LXmini
and Pluto at equal cone displacement levels to find correlations between
physics and perception. |
G2 - Power amplifier
distortion at 1 W & 100 mW output
| I recently changed to the AT528NC
power amplifier for my LX521.4
system in Sea Ranch. The amplifier delivers 8 x 200W into 8 ohm and is
based on Hypex NCore 500 Class-D modules. I had observed in the past that
my 2-tone, 1 kHz and 5.5 kHz, intermodulation test at 1 W output power
seemed to correlate with perceived amplifier sound quality. Distortion
products of these two frequencies fall into the frequency range between 1
kHz and 10 kHz, where the ear is most sensitive. Typical class A/B power
amplifiers have decreasing feedback loop gain in this frequency range,
which may affect their sound.
The test method using ARTA
and a Focusrite
Scarlett 2i2 is shown below with voltages for a 1 W measurement.
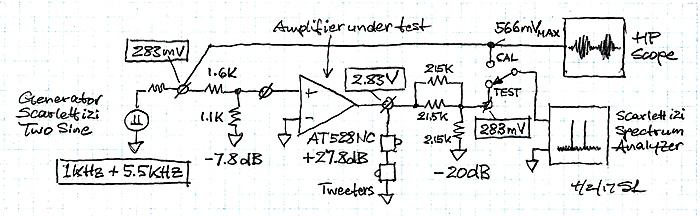
The Scarlett i2i sees the same voltages for
calibration as it does for test of the power amplifier in order to
maximize measurement range.
The unbalanced amplifier input was used.
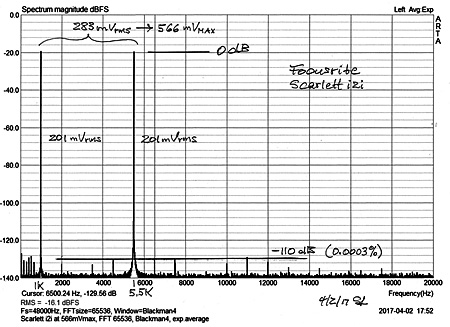

The 1 W measurement indicates superb performance of
the amplifier, as does the 100 mW measurement.
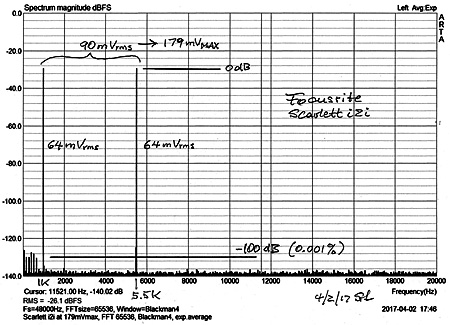
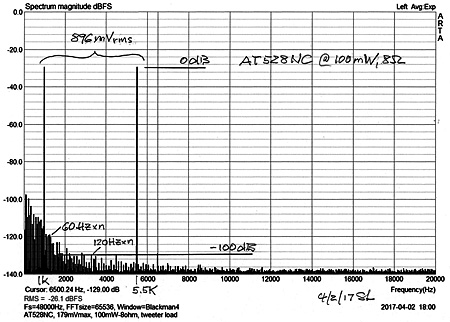
I have never measured a power amplifier with such low
distortion before.
See also: Other
Power Amplifiers |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Page 1 | Page 2
|
Page 3 | Page 4 | Page
5 | Page 6 | Page 7 |
|










